
Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2026-01-26 Origin: Site
Knowing how to choose rccb for every application is essential for greater safety, compliance, and operational efficiency. Selecting the wrong rccb exposes systems to electrical faults, risking electric shocks or fires, and can trigger costly maintenance and legal issues. HAIPART’s advanced rccb solutions deliver reliable protection across residential, commercial, industrial, and renewable energy applications. Electrical professionals trust our RCCB Selection Guide for Electrical Professionals to match the right rccb to every environment and requirement.
HAIPART combines over 30 years of experience with innovative rccb technology for greater safety and peace of mind.
Choosing the right RCCB type is crucial for safety, compliance, and operational efficiency in electrical systems.
RCCBs detect electrical faults and disconnect power quickly, preventing electric shocks and fire hazards.
Different applications require specific RCCB types to address unique risks and load characteristics.
Using the wrong RCCB can lead to serious safety risks, including electric shocks and legal issues.
Regular testing and maintenance of RCCBs ensure they function correctly and provide ongoing protection.
Always match the RCCB type and sensitivity to the specific application to maximize safety.
Consult with a qualified professional for complex installations to ensure proper selection and compliance.
Stay informed about international standards to guarantee that your RCCB meets safety requirements.
A residual current circuit breaker is a specialized device designed for protection against electrical faults. It plays a vital role in electrical safety by detecting residual current and disconnecting the power supply when leakage occurs. The operating principle of an rccb relies on continuous monitoring of the current flow through both live and neutral conductors. The device uses a differential current transformer to compare the currents. If the sum of the currents does not equal zero, the rccb identifies a residual current, which signals a fault.
The current in the live wire should match the current in the neutral wire.
Any earth fault causes current to flow to the ground, reducing the returning current in the neutral wire.
The rccb senses and compares the difference, known as residual current, and trips the circuit if an imbalance is detected.
The device operates using electromagnetic induction, with a magnetic core encasing the conductors. Balanced currents cancel each other’s magnetic fields, but leakage creates an imbalance, triggering the tripping mechanism.
This process ensures personal protection by disconnecting the circuit within milliseconds, preventing electric shocks and fire hazards. The rccb vs mcb comparison highlights that only the rccb can detect earth faults, making it essential for comprehensive protection.
Selecting the correct residual current circuit breaker is critical for maintaining safety standards and ensuring reliable protection. Different applications require specific rccb types to address unique risks and load characteristics. For example, electromagnetic rccb models can detect extremely small leakage currents, providing enhanced protection in sensitive environments. The right choice supports personal protection, compliance with safety standards, and effective power distribution.
Tip: Always match the rccb type to the application and load type to guarantee optimal protection and adherence to safety standards.
Proper selection also impacts the effectiveness of protection in residential, commercial, and industrial settings. The rccb vs rcbo comparison shows that while both devices offer protection, the rcbo combines residual current and overcurrent protection, making it suitable for circuits with mixed requirements. However, the rccb remains the preferred choice for dedicated residual protection.
Using the wrong rccb type can compromise safety and violate safety standards. Standard circuit breakers do not detect earth faults, which are the leading cause of residential electrical accidents. Even a small residual current, such as 30 milliamps, can cause cardiac arrest, while 50 milliamps may be fatal with prolonged exposure. The gap between the current that can harm a person and the threshold that trips a standard breaker is significant.
Earth faults allow sustained current flow through vital organs, increasing the risk of fatal outcomes.
Electrical codes worldwide now require rccb protection in high-risk areas due to the inability of standard breakers to protect against earth faults.
Failure to select the correct residual current circuit breaker can result in non-compliance with safety standards, increased liability, and reduced personal protection.
Choosing the right rccb ensures electrical safety, meets safety standards, and delivers reliable protection for people and property. The rccb vs rcbo and rccb vs mcb distinctions reinforce the importance of understanding device capabilities and application needs.
The ac type rccb is the most widely used device for basic electrical protection. Its features include detection of residual sinusoidal alternating current faults. The design focuses on simplicity and reliability, making it suitable for standard installations. These features ensure that the ac type rccb responds quickly to leakage currents, providing essential protection for people and property. The device operates efficiently with resistive loads and traditional AC motors. The features of this rccb type make it a preferred choice for environments with minimal electronic equipment.
Despite its robust features, the ac type rccb has limitations in modern electrical systems. It cannot detect faults with DC components or high-frequency distortion. Devices such as solar inverters, induction cooktops, and LED drivers may generate leakage currents outside the detection range of ac type rccb. These limitations mean that advanced protection is necessary for installations with complex loads.
The ac type rccb is best suited for basic residential applications. It provides reliable protection for simple appliances and standard AC motors. Electricians often choose this rccb type for environments where only sinusoidal AC currents are present. The features of the ac type rccb make it ideal for traditional homes and small offices.
Tip: Always verify the load characteristics before selecting ac type rccb for protection.
The a type rccb offers enhanced features compared to the ac type rccb. It detects both AC and pulsating DC leakage faults. This rccb type is designed for installations with electronic equipment, such as computers and appliances that produce pulsating DC currents. The features of the a type rccb include improved sensitivity and faster response times. It provides protection against a wider range of faults, ensuring safety in environments with mixed loads.
While the a type rccb has advanced features, it may not detect pure DC faults or high-frequency distortions. The device is not suitable for installations with equipment like solar inverters or variable-frequency drives that generate complex leakage currents. Electricians must consider these limitations when choosing the right rccb type for protection.
The a type rccb is ideal for residential and commercial installations with modern electronic devices. It provides protection for computers, washing machines, and other appliances that produce pulsating DC currents. The features of this rccb type make it a reliable choice for environments with mixed AC and DC loads.
The f type rccb introduces specialized features for environments with variable frequency drives and power electronics. It detects mixed frequencies, including subharmonic and supraharmonic currents. The features of the f type rccb address issues like blinding and nuisance tripping, which are common in systems with waveform distortion. This rccb type ensures protection in low voltage systems with complex load profiles.
The f type rccb may not be necessary for basic residential or commercial applications. Its features are tailored for specialized industrial settings. Electricians should assess the need for advanced protection before selecting this rccb type.
The f type rccb is best suited for industrial environments with variable frequency drives and equipment that generate waveform distortion. Its features provide reliable protection against a wide range of faults. This rccb type is essential for installations where standard devices may fail to detect complex leakage currents.
| RCCB Type | Detection Capabilities | Application Suitability |
|---|---|---|
| Type AC | Detects AC leakage faults only | Basic residential applications |
| Type A | Detects AC and pulsating DC leakage faults | Installations with equipment like computers and appliances that produce pulsating DC |
| Type F | Detects mixed frequencies | Specialized industrial settings with variable speed drives or similar equipment |
The rccb models comparison above highlights the unique features and protection capabilities of each type. Selecting the right rccb type ensures optimal protection and compliance with safety standards.
The b type rccb stands out as the most advanced solution for comprehensive protection in modern electrical systems. This rccb detects both AC and DC residual currents, which ensures a higher level of protection against electrical faults. The dual detection capability allows the b type rccb to respond to leakage currents from a wide range of sources, including electronic devices and renewable energy systems. Enhanced safety features help prevent electric shock and fire hazards, especially in environments where DC leakage is possible. The b type rccb meets international safety standards, making it suitable for residential, commercial, and industrial installations. Fast tripping times and high sensitivity provide reliable protection for people and property.
Note: The b type rccb is essential for installations with mixed AC/DC loads, such as solar power systems and EV charging stations.
The following table summarizes the advanced protection capabilities and typical installation environments for the b type rccb:
| Feature/Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Dual Detection Capability | Detects both AC and DC residual currents for broader protection. |
| Enhanced Safety | Prevents electric shock and fire by detecting DC leakage. |
| Standards Compliant | Meets international safety standards for residential and commercial use. |
| Solar Power Generation Systems | Ensures protection in installations with DC current from solar panels. |
| EV Charging Stations | Prevents electrical failures in electric vehicle charging stations. |
| Industrial Equipment | Provides protection for machines that may generate DC leakage current. |
The b type rccb offers advanced protection, but it may not be necessary for every application. This rccb is typically more complex and may require careful installation and maintenance. Electricians should assess the specific needs of each environment before selecting the b type rccb. In basic residential settings with only standard AC loads, other rccb types may provide sufficient protection. The b type rccb is designed for environments where DC leakage is a real risk, such as renewable energy systems and industrial equipment.
The b type rccb is the preferred choice for applications that demand the highest level of protection. It is essential in solar power generation systems, where DC currents are present. EV charging stations rely on the b type rccb to prevent electrical failures and ensure user safety. Industrial environments with equipment that may generate DC leakage currents benefit from the advanced protection provided by this rccb. Commercial buildings with mixed AC/DC loads also require the b type rccb for reliable protection.
Solar power installations
EV charging infrastructure
Industrial machinery with DC components
Commercial buildings with advanced electronic systems
Electrical professionals should select the b type rccb when comprehensive protection is required. This rccb ensures compliance with safety standards and delivers peace of mind in complex electrical environments.
Sensitivity and tripping characteristics define how quickly and effectively an rccb responds to electrical faults. Sensitivity refers to the minimum leakage current that triggers the device, while tripping time measures how fast the rccb disconnects the circuit. High sensitivity ensures maximum safety, especially in environments where personal protection is critical. The following table summarizes the main sensitivity ratings and their corresponding trip times:
| Sensitivity Rating | Trip Time at IΔn | Trip Time at 5×IΔn | Application Priority |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10mA | ≤ 300ms | ≤ 40ms | Maximum personal protection |
| 30mA | ≤ 300ms | ≤ 40ms | Standard personal protection |
| 100mA | ≤ 300ms | ≤ 40ms | Equipment + fire protection |
| 300mA | ≤ 300ms (or 150ms for Type S) | ≤ 40ms | Fire protection |
| 300mA Type S | ≤ 500ms | ≤ 150ms | Selective fire protection |
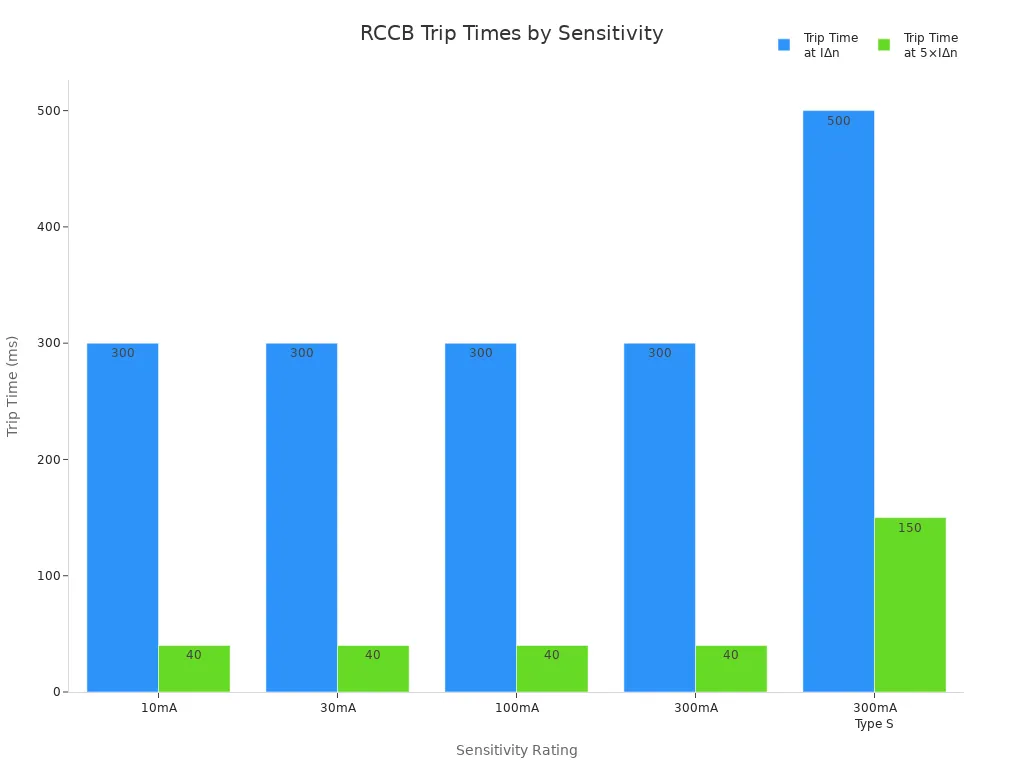
A 10mA rccb provides the highest level of personal protection, making it suitable for medical facilities or areas with vulnerable individuals. The 30mA rccb is the standard for residential safety, offering reliable protection against electric shock. Higher ratings, such as 100mA or 300mA, focus on equipment and fire protection, ensuring safety in commercial and industrial settings.
Compatibility with different load types is essential for selecting the right rccb. Not all devices can detect both alternating current and direct current leakage. The technical design of each rccb type determines its application range and level of protection. The table below outlines the compatibility of common rccb types:
| RCD Type | Compatible Loads | Technical Details |
|---|---|---|
| Type A | AC, Pulsating DC | Suitable for alternating sinusoidal residual current and residual pulsating direct current up to 6 mA. |
| Type F | AC, Type A | Used for frequency controlled appliances and equipment. |
| Type B | AC, Type A, Type F | Suitable for single and three-phase equipment, including those with DC components. |
Type A rccb units handle both AC and pulsating DC, making them ideal for modern homes with electronic devices. Type F rccb models extend protection to frequency-controlled appliances, such as variable speed drives. Type B rccb offers the broadest protection, covering AC, pulsating DC, and pure DC, which is essential for renewable energy systems and EV charging stations. This compatibility ensures safety and reliable protection across diverse applications.
Cost and performance play a significant role in rccb selection. The right choice balances budget, safety, and protection requirements. For residential installations, a basic 2-pole rccb with 30mA sensitivity delivers standard protection at an affordable price. Commercial environments often require 4-pole models with higher current ratings and advanced features for enhanced safety. Industrial applications demand rccb units with greater breaking capacity and specialized protection.
| Brand | Best For | Key Strengths |
|---|---|---|
| Schneider | Industrial plants | High fault tolerance (10kA+) |
| ABB | Commercial buildings | Modular DIN-rail integration |
| Legrand | Residential complexes | Compact space-saving design |
| CNC | Value-focused projects | Balance of performance & affordability |
Basic 2P 30mA: ₹800 - ₹2,500 – Standard for home use
Industrial 4P 100mA: ₹8,000+ – Advanced features, higher breaking capacity
Sensitivity 10mA: ₹2,000+ – Medical-grade, extra sensitive
Breaking Capacity 6kA: ₹800 - ₹2,500 – Good for most home and small office needs
Breaking Capacity 10kA+: ₹2,000+ – Premium, advanced protection
Selecting the right rccb ensures optimal safety and protection for people, equipment, and property. Matching the device to the application type, load characteristics, and budget guarantees reliable performance and compliance with safety standards.
International standards play a critical role in ensuring the safety and reliability of every rccb. These standards define the technical requirements, testing methods, and performance benchmarks that manufacturers must meet. Compliance with these standards guarantees that each rccb delivers consistent protection in a wide range of environments.
The most widely recognized standard for rccb devices is IEC 61008-1. This standard sets out the essential criteria for residual current operated circuit-breakers without integral overcurrent protection. It specifies how an rccb must detect ground fault currents and respond quickly to prevent electric shock. The standard applies to rccb units used in homes, commercial buildings, and similar installations. By following IEC 61008-1, manufacturers ensure that their rccb products provide reliable protection by disconnecting circuits within milliseconds when leakage currents exceed safe limits.
Another important standard is IEC 62423. This standard covers rccb types that must detect both AC and DC residual currents. It is especially relevant for advanced rccb models, such as Type B, which are used in renewable energy systems and installations with mixed AC/DC loads. IEC 62423 ensures that these rccb devices offer comprehensive protection, even in complex electrical environments.
Key requirements from these standards include:
Accurate detection of residual current imbalances between phase and neutral conductors.
Fast tripping action to disconnect power before dangerous shock levels occur.
Rigorous testing procedures to verify performance under various fault conditions.
Clear labeling and documentation for safe installation and maintenance.
| Standard | Scope | Application Areas |
|---|---|---|
| IEC 61008-1 | RCCBs without overcurrent protection | Residential, commercial |
| IEC 62423 | RCCBs for AC and DC residual current | Industrial, renewable energy, EV |
Manufacturers like HAIPART design their rccb solutions to meet or exceed these international standards. This commitment ensures that every rccb provides dependable protection for people and property. Electrical professionals can trust that compliant rccb devices will perform as expected, regardless of the installation environment.
Note: Always verify that the selected rccb carries certification to the relevant international standard. This step is essential for ensuring legal compliance and optimal protection.
Choosing an rccb that meets international standards is not just about following regulations. It is about guaranteeing the highest level of protection for every application. Proper compliance supports safety, reduces liability, and builds confidence in the electrical system.
Selecting the right rccb for residential environments is a critical step in the rccb selection guide for electrical professionals. Home installations require protection against electric shock and fire hazards. The process begins with understanding the types of rccb available. Standalone devices and integrated models offer different levels of protection. Most homes benefit from rccb units with a sensitivity rating of 30mA, which provides reliable protection for people.
Electricians must assess the rated current, typically between 16A and 63A, to match household needs. Type AC rccb is suitable for circuits with only alternating current. Type A rccb is recommended for homes with electronic devices that may produce pulsating direct current. Bathrooms and kitchens present higher risks due to water exposure. In these areas, consulting a licensed electrician ensures proper installation and protection.
Common rccb types used in residential applications include:
| Type of RCCB | Description |
|---|---|
| Residual Current Circuit Breakers with Overcurrent Protection | Combines rccb and overcurrent protection, trips on earth leakage or overload. |
| Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters | Detects earth leakage, ideal for wet areas, can be portable. |
Factors influencing rccb selection in homes:
Overcurrent characteristics must match the expected load.
Tripping characteristics should align with the application scenarios to avoid unwanted service interruptions.
Proper sizing and secure connections help prevent false alarms.
Tip: For maximum protection, always choose an rccb with the correct sensitivity and rated current for each circuit.
Commercial buildings present unique challenges for rccb selection. The rccb selection guide for electrical professionals recommends evaluating load diversity and the presence of sensitive equipment. Offices, retail spaces, and public facilities often use a mix of lighting, HVAC systems, and electronic devices. Protection requirements vary based on the complexity of the installation.
Type A rccb units are preferred for commercial installations with computers and appliances that generate pulsating DC currents. For areas with frequency-controlled equipment, Type F rccb offers enhanced protection. Electricians should consider selective discrimination to minimize service disruption during faults. The rated current for commercial rccb typically ranges from 25A to 63A, depending on the size of the facility.
Key steps for commercial rccb selection:
Assess the total load and select an rccb with adequate rated current.
Match the tripping curve to the application scenarios to ensure reliable protection.
Use selective rccb models to prevent unnecessary outages in multi-circuit installations.
Install rccb devices in high-risk zones, such as kitchens, server rooms, and public restrooms.
Note: Regular testing and maintenance of rccb units in commercial buildings help maintain optimal protection and compliance with safety standards.
Industrial settings demand robust protection due to complex machinery and higher fault risks. The rccb selection guide for electrical professionals emphasizes the importance of choosing devices that can handle mixed AC/DC loads and high current ratings. Factories, workshops, and manufacturing plants often use equipment with variable frequency drives and power electronics.
Type F and Type B rccb models provide advanced protection in industrial environments. Type F rccb detects mixed frequencies and prevents nuisance tripping caused by waveform distortion. Type B rccb offers comprehensive protection for installations with DC components, such as solar inverters and heavy machinery.
Recommended steps for industrial rccb selection:
Identify the types of loads and select an rccb compatible with both AC and DC currents.
Choose a device with a high rated current, often exceeding 63A, to support large equipment.
Ensure the rccb meets international standards for industrial protection.
Install ground fault relays for additional monitoring in critical zones.
Unwanted tripping can disrupt operations and cause downtime. Proper sizing, secure connections, and regular maintenance reduce the risk of false alarms.
Callout: In industrial environments, always consult with a qualified professional to ensure the rccb installation meets safety and operational requirements.
The rccb selection guide for electrical professionals provides a structured approach for matching the right rccb to residential, commercial, and industrial applications. Careful consideration of load type, sensitivity, and installation scenarios ensures reliable protection across all environments.
Renewable energy systems present unique challenges for electrical safety. Solar photovoltaic arrays and wind installations often combine both AC and DC circuits. These environments require advanced protection to ensure system reliability and safeguard people and equipment. The presence of direct current components increases the risk of faults that standard devices may not detect.
Electrical professionals must select an rccb that can identify leakage currents in both AC and DC circuits. This capability is essential for preventing faults that could damage sensitive equipment or create safety hazards. In renewable energy systems, the rccb serves as a critical line of defense. It disconnects the circuit when it detects dangerous leakage, minimizing the risk of fire or electric shock.
Compliance with international standards such as IEC 62477-1 is mandatory for renewable installations. These standards specify the requirements for rccb devices used in environments with mixed current types. The right rccb ensures protection against faults that may arise from solar inverters, battery storage units, and wind turbines. HAIPART offers rccb solutions engineered for these demanding applications, providing reliable protection and peace of mind.
When designing a renewable energy system, consider the following steps for selecting the appropriate rccb:
Assess the System Configuration
Identify all sources of AC and DC currents. Determine if the installation includes solar panels, wind turbines, or hybrid systems.
Choose the Correct RCCB Type
Select an rccb capable of detecting both AC and DC leakage currents. Type B rccb is recommended for comprehensive protection in renewable energy environments.
Verify Sensitivity and Rated Current
Ensure the rccb matches the expected load and sensitivity requirements. Higher sensitivity provides better protection for personnel and equipment.
Confirm Compliance with Standards
Check that the selected rccb meets IEC 62477-1 and other relevant standards for renewable energy systems.
Plan for Routine Testing and Maintenance
Schedule regular inspections to maintain optimal protection and system performance.
Tip: Always consult with a qualified professional when installing rccb devices in renewable energy systems. Proper selection and installation are vital for long-term safety and reliability.
Electric vehicle charging stations and environments with mixed AC/DC loads demand specialized protection strategies. These installations often involve high currents and complex load profiles. The risk of DC leakage currents is significant, especially in multi-station charging networks and commercial parking garages.
Selecting the right rccb for EV charging infrastructure is essential for user safety and equipment longevity. Type B rccb offers the broadest detection capabilities, including sinusoidal AC, pulsating DC, and smooth DC currents. Type F rccb provides protection for composite residual currents and is suitable for installations with integrated DC fault detection. Type EV rccb is designed specifically for dedicated EV charging applications, offering protection against smooth DC currents above 6mA and AC up to 30mA.
The following table summarizes the recommended rccb types for EV charging and mixed AC/DC load environments:
| RCCB Type | Detection Capabilities | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Type B | Sinusoidal AC, Pulsating DC, Smooth DC, AC up to 1,000Hz | EV charging stations, Photovoltaic systems, Industrial installations, Medical equipment |
| Type F | AC, Pulsating DC, Composite residual currents | EV charging stations with integrated DC fault detection, Residential installations, Commercial buildings |
| Type EV | Smooth DC ≥6mA, AC up to 30mA | Dedicated EV charging installations, Multi-station charging networks, Parking garage charging infrastructure |
Electrical professionals should follow these steps when selecting rccb devices for EV charging and mixed load environments:
Evaluate the Charging Station Design
Determine the number of charging points and the expected load profile.
Select the Appropriate RCCB Type
Use Type B rccb for installations with significant DC leakage risk. Consider Type F or Type EV rccb for specialized applications.
Ensure Adequate Sensitivity
Choose an rccb with the correct sensitivity rating to provide effective protection for users and equipment.
Verify Compatibility with Equipment
Confirm that the rccb integrates seamlessly with charging station hardware and control systems.
Schedule Regular Testing
Implement routine testing procedures to maintain high levels of protection and system reliability.
Callout: HAIPART’s advanced rccb solutions are designed to meet the rigorous demands of EV charging and renewable energy installations. These products deliver robust protection, ensuring compliance with international standards and safeguarding both people and assets.
Electrical professionals need a systematic approach when selecting an rccb for any installation. The following checklist covers essential steps to ensure optimal protection and compliance:
Verify compliance with both regional and international standards. This guarantees the rccb meets safety and performance requirements for the intended environment.
Confirm the tripping speed of the rccb. Devices should disconnect the circuit within 30 milliseconds when residual current exceeds 30mA, providing rapid protection against electric shock.
Assess environmental ratings. Choose an rccb designed for reliable operation in the specific weather or ambient conditions of the installation site.
Look for advanced features such as self-testing functions and LED indicators. These features simplify maintenance and enhance ongoing protection.
Determine the rated residual current. Residential applications typically require 30mA sensitivity, while industrial settings may need higher ratings for effective protection.
Evaluate the installation environment. Select an rccb with sensitivity levels appropriate for the type of load and risk factors present.
Tip: Always match the rccb type and sensitivity to the application’s risk profile. This ensures maximum protection for people and equipment.
The table below provides a concise comparison of common circuit protection devices, highlighting their primary functions, current ratings, and typical applications. Use this reference to select the right rccb or related device for each scenario.
| Feature | MCB | MCCB | RCB/RCD/RCCB | RCBO |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Protection | Overload, Short Circuit | Overload, Short Circuit | Earth/Ground Fault (Electric Shock) | Overload, Short Circuit, Earth/Ground Fault |
| Current Rating | Low to Medium (up to ~125A) | Medium to High (up to several thousand A) | Low to Medium (typically up to ~100A) | Low to Medium (up to ~63A) |
| Application | Residential, Light Commercial | Commercial, Industrial, Main Distribution | Residential, Commercial (for shock protection) | Residential, Commercial (all-in-one circuit protection) |
Electrical professionals should use rccb devices for earth fault protection in residential and commercial environments. For installations requiring both overload and earth fault protection, RCBO units offer a comprehensive solution. MCCB devices suit high-capacity industrial systems, while MCBs are ideal for basic overload protection in homes and small offices.
Note: Selecting the correct rccb type is essential for effective protection and regulatory compliance. Always consult manufacturer documentation and local codes before installation.
Sensitivity is a critical parameter when selecting an rccb for any application. The sensitivity rating, measured in milliamperes (mA), determines how quickly the device responds to leakage currents. High-sensitivity rccb units, typically rated between 6 mA and 30 mA, offer rapid protection against even minor electrical faults. This low threshold is essential for human safety, as it ensures the device trips before dangerous currents can cause harm. In residential settings, a 30 mA rccb is standard for personal protection, while medical environments may require devices with even lower ratings. Low-sensitivity rccb models, with ratings starting at 100 mA and above, are designed for equipment protection and fire prevention. These units are less responsive to small leaks but provide robust protection for electrical infrastructure. Selecting the correct sensitivity ensures optimal safety and protection for both people and property.
The current rating and number of poles are fundamental factors in rccb selection. These parameters influence the device’s compatibility with the electrical system and its overall performance.
Voltage rating must match the installation requirements.
Current rating should be selected based on the expected load, with 30 mA sensitivity recommended for personal protection.
Interrupting capacity determines the device’s ability to safely disconnect during faults.
Frequency compatibility ensures reliable operation in different environments.
Tripping current level adjustment ranges allow for tailored protection.
Environmental resistance supports safety in harsh conditions.
Number of poles must align with the system configuration, whether single-phase or three-phase.
Testing and maintenance features facilitate ongoing safety.
Proper setup guarantees effective protection.
The rated residual operating current is crucial for safety and protection.
Higher ratings may be necessary for equipment protection in industrial settings.
Compatibility with single-phase or three-phase systems is essential.
Always check the device’s voltage and breaking capacity to meet installation standards.
Choosing the right current rating and pole configuration ensures the rccb delivers reliable protection and maintains safety across diverse applications.
Device compatibility plays a significant role in rccb selection for modern electrical systems. Many contemporary devices, such as computers and variable-speed drives, generate non-sinusoidal currents. These currents can introduce harmonics, which may cause standard rccb units to trip unnecessarily. In environments with a high density of electronic equipment, specialized rccb models are required to handle these complex currents. Using the correct rccb type prevents nuisance tripping and ensures continuous protection. Electrical professionals must evaluate the types of loads present and select an rccb that matches the system’s requirements. This approach guarantees safety and protection for both users and equipment, especially in advanced installations.
Tip: Always assess the compatibility of the rccb with the connected devices to avoid unnecessary interruptions and maximize protection.
Environmental conditions play a critical role in the selection and long-term performance of any rccb. Electrical professionals must evaluate the installation site to ensure that the chosen rccb delivers consistent protection under all circumstances. Factors such as temperature, humidity, dust, vibration, and altitude can influence the reliability and effectiveness of protection systems.
Temperature extremes can cause derating or mechanical issues in rccb devices. High temperatures may reduce the lifespan of internal components, while low temperatures can affect tripping mechanisms. Selecting an rccb with a suitable temperature rating and providing adequate cooling or heating helps maintain optimal protection.
Humidity and moisture present significant risks. Excess moisture can lead to corrosion and insulation failure, compromising protection. Using rccb units with high ingress protection (IP) ratings and installing sealed enclosures ensures that the device remains reliable in damp environments.
Dust and debris can interfere with the mechanical and electrical operation of rccb products. Dust accumulation may block moving parts or cause electrical shorts, reducing protection. Installing rccb devices in dust-tight enclosures and scheduling regular cleaning helps prevent these issues.
Vibration and shock are common in industrial settings. These forces can misalign components or cause tripping failures. Choosing vibration-resistant rccb models and securing mounting hardware enhances protection and reduces the risk of malfunction.
Altitude affects cooling and increases the risk of electrical arcing. At higher elevations, air density decreases, which can impact the heat dissipation of rccb units. Derating the device and selecting models rated for high-altitude operation ensures consistent protection.
Corrosive environments, such as chemical plants or coastal areas, can degrade materials and compromise protection. Using corrosion-resistant rccb devices and sealed enclosures helps maintain safety standards.
Voltage fluctuations and poor power quality may cause false trips or failure to trip. Advanced trip units and surge protection devices (SPDs) improve the reliability of rccb protection in these scenarios.
Electromagnetic interference (EMI) can disrupt the operation of trip units. Shielding rccb devices and avoiding installation near high EMI sources ensures uninterrupted protection.
UV radiation can degrade the casing of rccb products, especially in outdoor installations. UV-resistant enclosures provide additional protection against sunlight exposure.
Aging and wear reduce the reliability of rccb protection over time. Regular maintenance and timely replacement are essential for maintaining safety.
The following table summarizes key environmental conditions, their impact on rccb operation, and recommended solutions:
| Environmental Condition | Impact | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Derating, mechanical issues | Select temperature-rated rccb, provide cooling/heating |
| Humidity and Moisture | Corrosion, insulation failure | Use high IP-rated rccb, sealed enclosures |
| Dust and Debris | Mechanical/electrical issues | Dust-tight enclosures, regular cleaning |
| Vibration and Shock | Misalignment, tripping failure | Vibration-resistant rccb, secure mounting |
| Altitude | Reduced cooling, arcing risk | Derate rccb, use high-altitude-rated models |
| Corrosive Environments | Material degradation | Corrosion-resistant rccb, sealed enclosures |
| Voltage and Power Quality | False trips, failure to trip | Advanced trip units, install SPDs |
| Electromagnetic Interference | Trip unit disruption | Shield rccb, avoid high EMI areas |
| UV Radiation | Casing degradation | UV-resistant enclosures |
| Aging and Wear | Reduced reliability | Regular maintenance, timely replacement |
Tip: Always assess environmental factors before selecting an rccb. Proper evaluation ensures that protection remains effective throughout the device’s service life.
Electrical professionals who consider these environmental aspects can optimize rccb selection and installation, guaranteeing robust protection for people and equipment in any setting.
Electrical professionals often encounter recurring issues during rccb selection and installation. These mistakes can compromise safety, reduce protection, and increase the risk of electrical hazards. Understanding these pitfalls is essential for effective fire prevention and reliable system operation.
One of the most frequent errors involves ignoring the specific load characteristics of an installation. Each rccb must match the type and size of the electrical load to deliver optimal protection. Selecting an rccb with an incorrect rating can result in nuisance tripping or, worse, inadequate protection against faults. For example, using a device rated for residential loads in an industrial environment may leave critical equipment unprotected. Professionals should always analyze the load profile, including the presence of electronic devices or mixed AC/DC currents, before choosing an rccb. This step ensures the device provides the necessary protection and supports overall safety.
Failing to assess load type can lead to false trips.
Mismatched ratings may allow dangerous leakage currents to persist.
Specialized environments, such as those with variable frequency drives, require advanced rccb models for comprehensive protection.
Tip: Always verify the compatibility of the rccb with the intended load to maximize safety and protection.
Another common mistake is disregarding the manufacturer's installation instructions and technical recommendations. Each rccb is designed with specific wiring requirements and operational parameters. Improper installation, such as incorrect wiring or bypassing safety features, can render the device ineffective. Adhering to manufacturer guidelines ensures the rccb functions as intended and maintains the highest level of protection. Professionals should consult product documentation and follow all regulatory standards during installation.
Incorrect wiring can prevent the rccb from detecting faults.
Skipping recommended installation steps may compromise protection.
Manufacturer guidelines often include important details for ongoing safety and device longevity.
Note: Following the manufacturer's instructions is a critical step in ensuring reliable protection and compliance with safety standards.
Neglecting regular maintenance and testing is a significant oversight that can undermine the effectiveness of any rccb. Over time, environmental factors and normal wear can affect device performance. Routine testing verifies that the rccb responds correctly to leakage currents and continues to provide essential protection. Scheduled maintenance helps identify potential issues before they escalate into safety hazards. Without these checks, even the best rccb may fail to deliver adequate protection when needed most.
Regular testing confirms the tripping mechanism operates properly.
Maintenance extends the service life of the rccb and supports ongoing safety.
Documenting test results helps track device performance and plan timely replacements.
Callout: Consistent maintenance and testing are vital for sustaining protection and ensuring long-term safety in every installation.
By avoiding these common mistakes, electrical professionals can enhance protection, support fire prevention, and uphold the highest standards of safety in all environments.
Correct installation of an rccb is essential for achieving maximum protection and long-term safety. Begin by selecting the right breaker switch that matches the electrical load. Consider voltage and circuit type before proceeding. Always use rccb devices together with miniature circuit breakers (MCBs) to enhance protection against both overloads and earth faults. A qualified professional should handle the installation to ensure compliance with local electrical codes and regulations. Secure all connections tightly and clean contacts to prevent overheating or corrosion. Position the rccb in an accessible location for easy testing and maintenance. Double-check the wiring to confirm that the device will detect residual currents accurately. Use the manufacturer’s guidelines to avoid errors during installation.
Tip: Proper installation of rccb units forms the foundation of a reliable protection system and supports ongoing safety for people and equipment.
Routine testing is vital for maintaining the effectiveness of rccb protection. Monthly testing using the built-in test button is recommended. This simple procedure verifies that the device trips correctly when a fault occurs. Treat every trip as a sign of a potential issue, such as electric leakage or faulty wiring. Address these problems promptly to maintain safety. Schedule regular check-ups to inspect for signs of wear, including corrosion or overheating. Test the switches periodically, especially in critical systems where protection is paramount. Document each test result to track performance and plan future maintenance. Clean the device and surrounding area to prevent dust buildup, which can affect operation.
| Testing Step | Frequency | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Press test button | Monthly | Confirms tripping mechanism |
| Visual inspection | Quarterly | Detects wear or corrosion |
| Connection check | Annually | Ensures tight, clean contacts |
| System review | Annually | Verifies overall protection |
Note: Regular testing and maintenance of rccb devices guarantee consistent protection and uphold safety standards in every environment.
Effective troubleshooting ensures that rccb protection remains reliable over time. If the rccb trips unexpectedly, investigate the cause immediately. Check for electric leakage, damaged insulation, or faulty appliances. Inspect connections for looseness or corrosion, which can compromise protection. Replace any worn or damaged components to restore safety. If the device fails to trip during testing, consult the manufacturer’s documentation or seek professional assistance. Keep a record of all troubleshooting actions to support future maintenance. Address environmental factors, such as humidity or dust, that may affect device performance.
Callout: Prompt troubleshooting and regular maintenance of rccb units are crucial for sustaining protection and ensuring long-term safety in all installations.
Electrical professionals can achieve optimal safety and protection by following these essential steps when selecting an rccb for any application:
Calculate the circuit load and include a safety margin for future expansion.
Match the rccb current rating to the cable capacity and application type.
Choose the correct rccb type for the environment, ensuring comprehensive protection for both AC and DC loads.
Consult the rccb selection guide and models comparison to confirm compatibility and compliance.
Reach out to HAIPART or a qualified expert for complex installations or advanced protection needs.
HAIPART’s rccb solutions deliver unmatched safety, reliable protection, and full compliance for residential, commercial, industrial, and renewable energy systems.
An rccb is a safety device that detects residual current caused by earth faults. It disconnects the circuit quickly to prevent electric shock and fire hazards. Electrical professionals rely on rccb units to maintain safety and meet compliance standards.
Select an rccb based on load type, sensitivity, and installation environment. Type AC suits basic residential use. Type A fits mixed loads. Type F and Type B provide advanced protection for industrial, renewable, or EV charging systems.
Type B rccb units detect both AC and DC residual currents. These models are essential for renewable energy systems, EV charging stations, and industrial setups with DC components. Type A and Type F rccb models offer limited DC protection.
Test your rccb monthly using the built-in test button. Regular testing ensures the device responds to faults and maintains protection. Document each test for future reference and schedule professional inspections annually.
A 30mA sensitivity rating is standard for residential rccb installations. This rating provides effective protection against electric shock. Higher sensitivity, such as 10mA, may be required in medical or high-risk environments.
Most electrical codes mandate rccb protection in residential, commercial, and industrial installations. Compliance ensures safety and reduces liability. Always verify local regulations before selecting and installing an rccb.
A licensed electrician should install an rccb. Proper installation guarantees reliable protection and compliance with safety standards. Incorrect wiring or setup may compromise device performance and safety.
Routine maintenance includes monthly testing, visual inspections, and cleaning. Check connections for corrosion or looseness. Replace any damaged components promptly. Regular maintenance extends the service life of your rccb and supports ongoing safety.